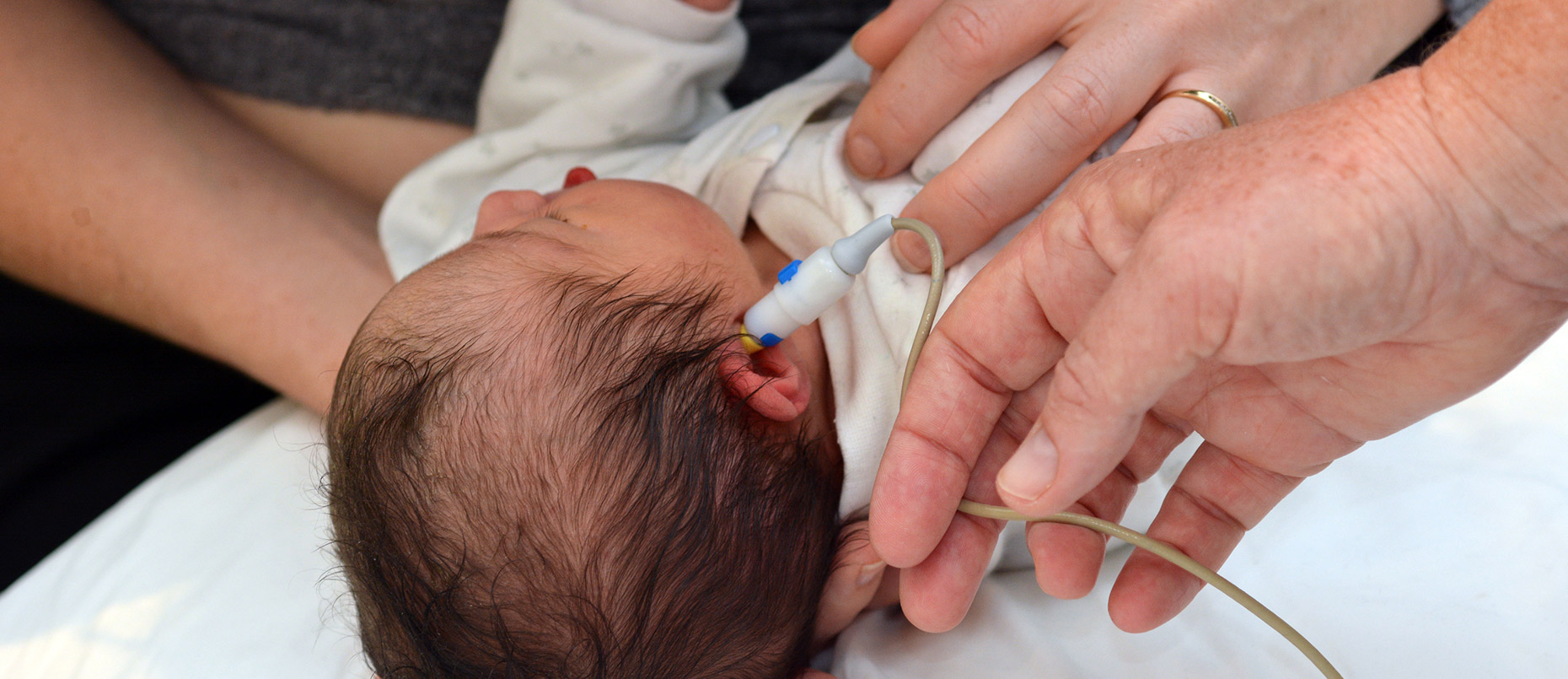
Hearing loss in newborns, also known as congenital hearing loss, is a condition where a baby is born with reduced hearing in one or both ears. This condition can have significant implications for a child’s language development and overall communication skills. Here is a comprehensive article on newborn hearing loss, covering its causes, diagnosis, treatment, and management

Causes of Newborn Hearing Loss
Newborn hearing loss can be attributed to various factors:
- Genetic Factors: Genetics is the leading cause of hearing loss in many babies. It can be syndromic, where hearing loss is associated with other medical issues, or non-syndromic, where hearing loss is the only condition present.
- Maternal Infections: Infections passed from the mother to the baby in the womb, such as toxoplasmosis, measles, or herpes, can lead to hearing loss.
- Birth Complications: Complications during birth, including asphyxia, low birth weight, and hyperbilirubinemia, can contribute to hearing loss.
- Ototoxic Medications: Medications that are toxic to the ear, such as certain antibiotics, can cause hearing loss.
- Infections After Birth: Postnatal infections like meningitis can damage the auditory nerve or the brain pathways leading to the nerve.
Diagnosis of Newborn Hearing Loss
Newborn hearing screening is a critical step in identifying hearing loss early. It is recommended that all babies be screened for hearing loss no later than 1 month of age, preferably before leaving the hospital after birth. If a baby does not pass the initial screening, a full hearing test, or audiology evaluation, should be conducted as soon as possible.
Treatment and Management
While there is no cure for congenital hearing loss, there are several interventions that can help manage the condition:
- Hearing Aids: For many types of hearing loss, hearing aids can amplify sounds and make them clearer, especially for infants, to support the development of speech skills.
- Cochlear Implants: In cases of severe to profound hearing loss, cochlear implants may be an option. These devices provide a way to hear when hearing aids are not enough.
- Early Intervention Services: These services are crucial for helping young children with hearing loss develop language skills. The earlier the intervention, the better the outcomes for the child’s development.
- Communication and Language Approaches: Various approaches, including sign language or cued speech, can be used depending on the family’s preferences and the child’s needs.
Prevention and Protection
- Preventive measures include maternal health care to avoid infections during pregnancy, reducing exposure to loud noises, and avoiding ototoxic medications when possible. It’s also important to monitor children’s hearing over time, as some forms of hearing loss may not become apparent until later in childhood.
Conclusion
- Newborn hearing loss is a condition that can significantly impact a child’s ability to communicate and develop language skills. Early detection through newborn hearing screening and subsequent interventions can greatly improve outcomes for children with hearing loss. Parents and caregivers should be vigilant for signs of hearing loss and seek professional advice if they have any concerns about their child’s hearing. With appropriate management and support, children with hearing loss can lead full and productive lives.